Why Brass Fasteners Are the Ideal Choice for Corrosion Resistance
Brass fasteners are highly valued for their durability, corrosion resistance, and excellent conductivity, making them a preferred choice across multiple industries. Manufactured from a copper-zinc alloy, these fasteners ensure long-lasting performance, even in harsh environments. Available in various types, brass fasteners cater to diverse applications, including electrical, marine, plumbing, and automotive industries.
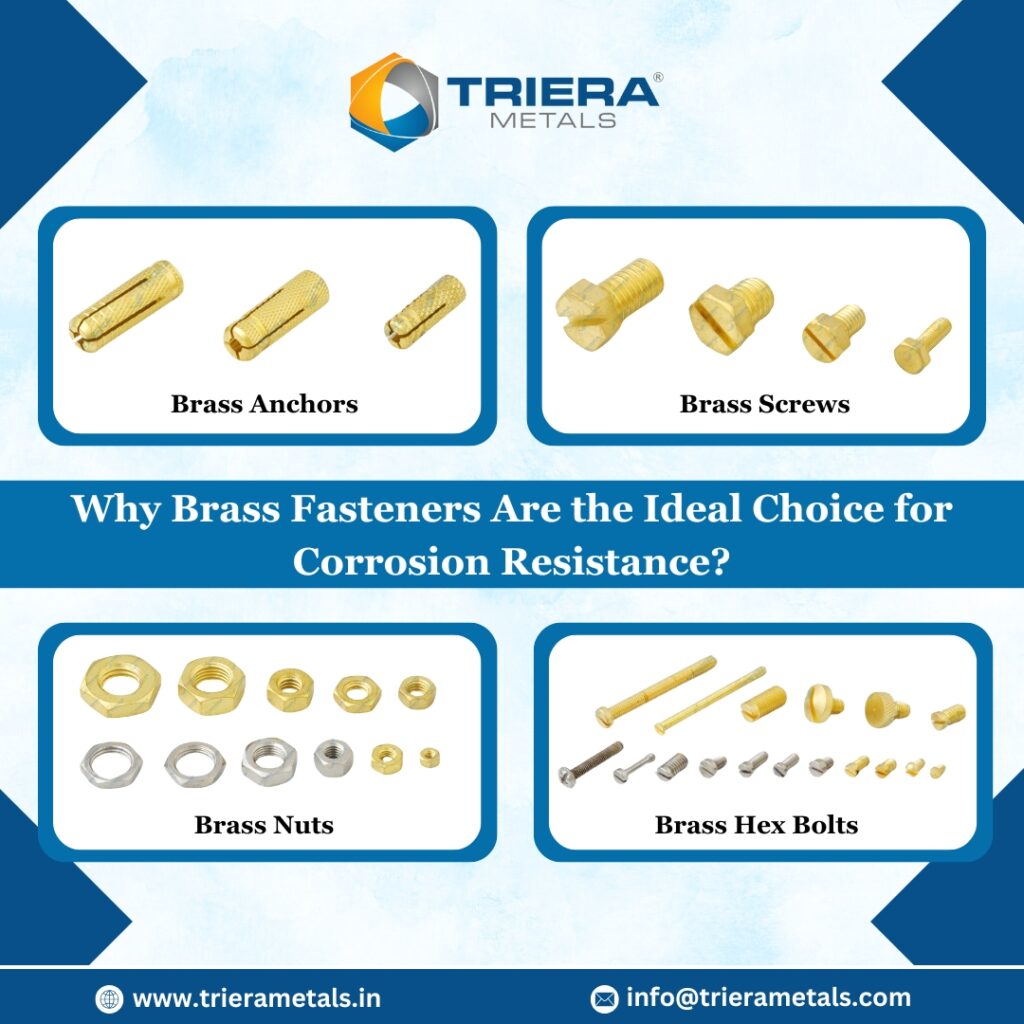
The different types of brass fasteners include:
- Brass Bolts – Used for secure fastening in structural and mechanical applications.
- Brass Hex Bolts – Provide a strong and reliable hold in heavy-duty applications.
- Brass Nuts – Ensure strong and corrosion-resistant joints in machinery and construction.
- Brass Screws – Ideal for wood, plastic, and metal applications, offering high tensile strength.
- Brass Anchors – Designed for heavy-duty fixing in concrete, brick, and masonry.
With their non-magnetic and anti-sparking properties, brass fasteners are a safe and reliable choice for various industries. In this blog, we will explore their advantages, applications, and why they remain a top choice for fastening needs.
Understanding Corrosion and Its Impact on Fasteners
Corrosion is the gradual deterioration of metal caused by environmental factors like moisture, chemicals, and salt exposure. In fasteners, corrosion weakens structural integrity, leading to safety risks and increased maintenance costs.
- Oxidation: Exposure to oxygen causes rusting in iron-based fasteners.
- Galvanic Corrosion: When two dissimilar metals come into contact, one corrodes faster than the other.
- Chemical Corrosion: Exposure to acids or industrial chemicals accelerates metal breakdown.
Why Brass is Highly Corrosion-Resistant
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, both of which provide excellent resistance to corrosion. Unlike steel, brass does not rust and forms a protective patina over time that prevents further degradation.
The key reasons brass resists corrosion include:
- Non-Ferrous Composition: Lacks iron, which eliminates the risk of rusting.
- Natural Oxide Layer: Forms a thin protective layer that prevents further oxidation.
- Resistance to Marine and Industrial Environments: Withstands exposure to saltwater and chemicals better than many other metals.
These properties make brass fasteners an ideal choice for demanding applications where corrosion can compromise structural integrity.
Benefits of Using Brass Fasteners
Brass fasteners offer numerous advantages beyond corrosion resistance:
- Durability: Maintains strength and performance over long periods.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Retains a polished, attractive appearance.
- Non-Magnetic Properties: Ideal for electronic and sensitive applications.
- Easy Machinability: Simplifies production and customization.
- High Thermal and Electrical Conductivity: Useful in electrical applications.
Common Applications of Brass Fasteners
Brass fasteners are widely used across multiple industries, including:
- Industry: Resistant to saltwater corrosion, making them ideal for boats and docks.
- Plumbing: Used in fittings and fixtures due to their resistance to water damage.
- Electrical Industry: Preferred for connectors and circuit boards because of their conductivity.
- Automotive Sector: Used in specialized applications where corrosion resistance is crucial.
- Construction: Utilized in architectural designs where aesthetics and durability matter.
Comparing Brass Fasteners with Other Materials
- Brass vs. Stainless Steel: Stainless steel is stronger, but brass offers superior machinability and electrical conductivity.
- Brass vs. Aluminum: Aluminum is lightweight, but brass is more corrosion-resistant in marine environments.
- Brass vs. Zinc-Plated Steel: Zinc plating provides temporary corrosion resistance, whereas brass offers long-term protection without additional coatings.
